What Is Pain In The Heel
Overview
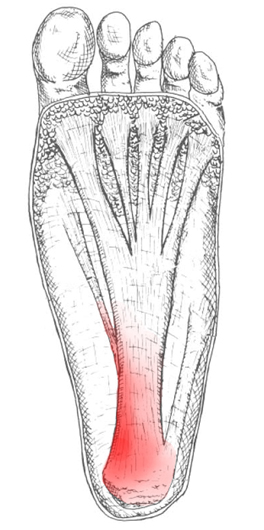
Foot pain affects nearly all people at one time or another. It can also lead to other musculoskeletal problems such as ankle, knee and back pain (Hill et al., 2008). This pain negatively affects one’s quality of life and ability to enjoy workouts and/or maintain a regular program of exercise. One of the most common sources of foot pain is plantar fasciitis, a condition where the connective tissue on the underside of the foot becomes irritated and painful as a result of an injury, overuse or misuse. The plantar fascia is a system of connective tissue that runs from your heel to just behind your toes. During weightbearing activities, such as walking or running, your body weight is transferred onto your foot from your heel to your toes (which results in your toes moving away from your heel). This spreading out of the foot places tension on the plantar fascia because it connects those two parts. If the tension on this structure is too great or is not dispersed evenly, the plantar fascia can develop microtears and become irritated and painful, resulting in a condition called plantar fasciitis.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis generally occurs over time, rather than being the result of a single event. Micro trauma from repetitive stress to the tissue often combines with a biomechanical deficiency of the foot to produce the condition. In addition, arthritic and metabolic factors may contribute to the development of this injury, (though they are unlikely to affect young athletes). A variety of training errors commonly lead to plantar fasciitis, particularly a rapid increase in either volume or intensity of athletic activity. Volume refers to the distance or time an athlete performs, while intensity refers to the pace of activity and/or the recovery time allowed following performance.
Symptoms
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis are pain on the bottom of the heel, pain in the arch of the foot, pain that is usually worse upon arising, pain that increases over a period of months. People with plantar fasciitis often describe the pain as worse when they get up in the morning or after they’ve been sitting for long periods of time. After a few minutes of walking the pain decreases, because walking stretches the fascia. For some people the pain subsides but returns after spending long periods of time on their feet.
Diagnosis
Most cases of plantar fasciitis are diagnosed by a health care provider who listens carefully to your description of symptoms. During an examination of your feet, your health care provider will have to press on the bottom of your feet, the area most likely to be painful in plantar fasciitis. Because the pain of plantar fasciitis has unique characteristics, pain upon rising, improvement after walking for several minutes, pain produced by pressure applied in a specific location on your foot but not with pressure in other areas, your health care provider will probably feel comfortable making the diagnosis based on your symptoms and a physical examination. Your health care provider may suggest that you have an X-ray of your foot to verify that there is no stress fracture causing your pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
About 90% of plantar fasciitis cases are self-limited and will improve within six months with conservative treatment and within a year regardless of treatment. Many treatments have been proposed for the treatment of plantar fasciitis. First-line conservative approaches include rest, heat, ice, calf-strengthening exercises, techniques to stretch the calf muscles, achilles tendon, and plantar fascia, weight reduction in the overweight or obese, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. NSAIDs are commonly used to treat plantar fasciitis, but fail to resolve the pain in 20% of people. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is an effective treatment modality for plantar fasciitis pain unresponsive to conservative nonsurgical measures for at least three months. Corticosteroid injections are sometimes used for cases of plantar fasciitis refractory to more conservative measures. The injections may be an effective modality for short-term pain relief up to one month, but studies failed to show effective pain relief after three months. Notable risks of corticosteroid injections for plantar fasciitis include plantar fascia rupture, skin infection, nerve or muscle injury, or atrophy of the plantar fat pad. Custom orthotic devices have been demonstrated as an effective method to reduce plantar fasciitis pain for up to 12 weeks. Night splints for 1-3 months are used to relieve plantar fasciitis pain that has persisted for six months. The night splints are designed to position and maintain the ankle in a neutral position thereby passively stretching the calf and plantar fascia overnight during sleep. Other treatment approaches may include supportive footwear, arch taping, and physical therapy.

Surgical Treatment
When more-conservative measures aren't working, your doctor might recommend steroid shots. Injecting a type of steroid medication into the tender area can provide temporary pain relief. Multiple injections aren't recommended because they can weaken your plantar fascia and possibly cause it to rupture, as well as shrink the fat pad covering your heel bone. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy. In this procedure, sound waves are directed at the area of heel pain to stimulate healing. It's usually used for chronic plantar fasciitis that hasn't responded to more-conservative treatments. This procedure may cause bruises, swelling, pain, numbness or tingling and has not been shown to be consistently effective. Surgery. Few people need surgery to detach the plantar fascia from the heel bone. It's generally an option only when the pain is severe and all else fails. Side effects include a weakening of the arch in your foot.
Stretching Exercises
The following exercises are commonly prescribed to patients with this condition. You should discuss the suitability of these exercises with your physiotherapist prior to beginning them. Generally, they should be performed 2 - 3 times daily and only provided they do not cause or increase symptoms. Your physiotherapist can advise when it is appropriate to begin the initial exercises and eventually progress to the intermediate and advanced exercises. As a general rule, addition of exercises or progression to more advanced exercises should take place provided there is no increase in symptoms. Calf Stretch with Towel. Begin this stretch in long sitting with your leg to be stretched in front of you. Your knee and back should be straight and a towel or rigid band placed around your foot as demonstrated. Using your foot, ankle and the towel, bring your toes towards your head until you feel a stretch in the back of your calf, Achilles tendon, plantar fascia or leg. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times at a mild to moderate stretch provided the exercise is pain free. Resistance Band Calf Strengthening. Begin this exercise with a resistance band around your foot as demonstrated and your foot and ankle held up towards your head. Slowly move your foot and ankle down against the resistance band as far as possible and comfortable without pain, tightening your calf muscle. Very slowly return back to the starting position. Repeat 10 - 20 times provided the exercise is pain free.