Is Over-Pronation
Overpronation and underpronation describe general foot movements. These terms do not necessarily describe a medical problem with a foot. For example, you can overpronate and not have any problems or symptoms at all. It is important to have your foot structure and symptoms adequately assessed by your prescribing physician and a qualified practitioner such as a Canadian Certified Pedorthist. Once the underlying conditions and mechanical faults are assessed, an appropriate treatment plan including possible orthotic and footwear recommendations can be made.

Causes
Generally fallen arches are a condition inherited from one or both parents. In addition, age, obesity, and pregnancy cause our arches to collapse. Being in a job that requires long hours of standing and/or walking (e.g. teaching, retail, hospitality, building etc) contributes to this condition, especially when standing on hard surfaces like concrete floors. Last, but not least unsupportive footwear makes our feet roll in more than they should.
Symptoms
Overpronation may have secondary effects on the lower legs, such as increased rotation of the tibia, which may result in lower leg or knee problems. Overpronation is usually associated with many overuse injuries in running including medial tibial stress syndrome, or shin splints, and knee pain Individuals with injuries typically have pronation movement that is about two to four degrees greater than that of those with no injuries. Between 40% and 50% of runners who overpronate do not have overuse injuries. This suggests that although pronation may have an effect on certain injuries, it is not the only factor influencing their development.
Diagnosis
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and activities and examine your feet. Your provider may watch you walk or run. Check the motion of your feet when they strike the ground. Look at your athletic shoes to see if they show an abnormal pattern of wear.

Non Surgical Treatment
Over-Pronation can be treated conservatively (non-surgical treatments) with over-the-counter orthotics. These orthotics should be designed with appropriate arch support and medial rearfoot posting to prevent the over-pronation. Footwear should also be examined to ensure there is a proper fit. Footwear with a firm heel counter is often recommended for extra support and stability. Improperly fitting footwear can lead to additional foot problems.
Prevention
Wearing the proper footwear plays a key role as a natural way to help pronation. Pronated feet need shoes that fit well, provide stability, contain supportive cushioning, are comfortable and allow enough room for your foot to move without causing pain or discomfort. Putting special inner heel wedges, known as orthotics, into your shoes can support a flatfoot while lowering risks of developing tendinitis, according to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. More extensive cases may require specially fitted orthopaedic shoes that support the arches.
How Do I Deal With Calcaneal Apophysitis In The Home?
It is thought to be a traction injury, where the Achilles tendon and Plantar fascia pull in opposite directions. Sever?s occurs in children aged 8 to 16 years old. In children, the heel bone is made up of 2 bones, with a growth plate of cartilage in between the sections, holding these 2 bones together. As the cartilage expands, the edges of it eventually turn to bone, and finally the gap closes. This usually occurs within the first 13-15 years of life. However, because these bones are connected by cartilage they are weaker than normal bones. This is why they are very vulnerable to injury.
Causes
This condition is more common in boys than girls. It generally presents between the ages of 9-14 and peaks between ages 10-12 years. This injury can reoccur up until the age of 17, when the growth plate of the calcaneous generally closes. These types of injuries will commonly occur during periods of rapid growth. Sever?s Disease occurs more frequently in child with flat feet, but all children with flat feet will not get Sever?s.
Symptoms
Symptoms of calcaneal apophysitis may include pain in the back or bottom of the heel, Limping, walking on toes, difficulty running, jumping, or participating in usual activities or sports. Pain when the sides of the heel are squeezed.
Diagnosis
Sever?s disease can be diagnosed based on your history and symptoms. Clinically, your physiotherapist will perform a "squeeze test" and some other tests to confirm the diagnosis. Some children suffer Sever?s disease even though they do less exercise than other. This indicates that it is not just training volume that is at play. Foot and leg biomechanics are a predisposing factor. The main factors thought to predispose a child to Sever?s disease include decrease ankle dorsiflexion, abnormal hind foot motion eg overpronation or supination, tight calf muscles, excessive weight-bearing activities eg running.
Non Surgical Treatment
stretching exercises can help. It is important that your child performs exercises to stretch the hamstring and calf muscles, and the tendons on the back of the leg. The child should do these stretches 2 or 3 times a day. Each stretch should be held for about 20 seconds. Both legs should be stretched, even if the pain is only in 1 heel. Your child also needs to do exercises to strengthen the muscles on the front of the shin. To do this, your child should sit on the floor, keeping his or her hurt leg straight. One end of a bungee cord or piece of rubber tubing is hooked around a table leg. The other end is hitched around the child's toes. The child then scoots back just far enough to stretch the cord. Next, the child slowly bends the foot toward his or her body. When the child cannot bend the foot any closer, he or she slowly points the foot in the opposite direction (toward the table). This exercise (15 repetitions of "foot curling") should be done about 3 times. The child should do this exercise routine a few times daily.
Cause Of Acquired Flat Foot
Overview
PTTD is most commonly seen in adults and referred to as "adult acquired flatfoot". Symptoms include pain and swelling along the inside arch and ankle, loss of the arch height and an outward sway of the foot. If not treated early, the condition progresses to increased flattening of the arch, increased inward roll of the ankle and deterioration of the posterior tibial tendon. Often, with end stage complications, severe arthritis may develop. How does all this happen? In the majority of cases, it is overuse of the posterior tibial tendon that causes PTTD. And it is your inherited foot type that may cause a higher possibility that you will develop this condition. 
Causes
Several risk factors are associated with PTT dysfunction, including high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, previous ankle surgery or trauma and exposure to steroids. A person who suspects that they are suffering from PTT dysfunction should seek medical attention earlier rather than later. It is much easier to treat early and avoid a collapsed arch than it is to repair one. When the pain first happens and there is no significant flatfoot deformity, initial treatments include rest, oral anti-inflammatory medications and, depending on the severity, a special boot or brace.
Symptoms
Your feet tire easily or become painful with prolonged standing. It's difficult to move your heel or midfoot around, or to stand on your toes. Your foot aches, particularly in the heel or arch area, with swelling along the inner side. Pain in your feet reduces your ability to participate in sports. You've been diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis; about half of all people with rheumatoid arthritis will develop a progressive flatfoot deformity.
Diagnosis
Clinicians need to recognize the early stage of this syndrome which includes pain, swelling, tendonitis and disability. The musculoskeletal portion of the clinical exam can help determine the stage of the disease. It is important to palpate the posterior tibial tendon and test its muscle strength. This is tested by asking patient to plantarflex and invert the foot. Joint range of motion is should be assessed as well. Stiffness of the joints may indicate longstanding disease causing a rigid deformity. A weightbearing examination should be performed as well. A complete absence of the medial longitudinal arch is often seen. In later stages the head of the talus bone projects outward to the point of a large "lump" in the arch. Observing the patient's feet from behind shows a significant valgus rotation of the heel. From behind, the "too many toes" sign may be seen as well. This is when there is abducution of the forefoot in the transverse plane allowing the toes to be seen from behind. Dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon can be assessed by asking the patient to stand on his/her toes on the affected foot. If they are unable to, this indicates the disease is in a more advanced stage with the tendon possibly completely ruptured.
Non surgical Treatment
Because of the progressive nature of PTTD, early treatment is advised. If treated early enough, your symptoms may resolve without the need for surgery and progression of your condition can be arrested. In contrast, untreated PTTD could leave you with an extremely flat foot, painful arthritis in the foot and ankle, and increasing limitations on walking, running, or other activities. In many cases of PTTD, treatment can begin with non-surgical approaches that may include. Orthotic devices or bracing. To give your arch the support it needs, your foot and ankle surgeon may provide you with an ankle brace or a custom orthotic device that fits into the shoe. Immobilization. Sometimes a short-leg cast or boot is worn to immobilize the foot and allow the tendon to heal, or you may need to completely avoid all weight-bearing for a while. Physical therapy. Ultrasound therapy and exercises may help rehabilitate the tendon and muscle following immobilization. Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, help reduce the pain and inflammation. Shoe modifications. Your foot and ankle surgeon may advise changes to make with your shoes and may provide special inserts designed to improve arch support. 
Surgical Treatment
Good to excellent results for more than 80% of patients have been reported at five years' follow up for the surgical interventions recommended below. However, the postoperative recovery is a lengthy process, and most surgical procedures require patients to wear a plaster cast for two to three months. Although many patients report that their function is well improved by six months, in our experience a year is required to recover truly and gain full functional improvement after the surgery. Clearly, some patients are not candidates for such major reconstructive surgery.
Heel Pain And Discomfort

The most common form of Heel Pain, is pain on the bottom of the heel. It tends to occur for no apparent reason and is often worse when first placing weight on the foot. Patients often complain of pain the first thing in the morning or after getting up to stand after sitting. The pain can be a sharp, searing pain or present as a tearing feeling in the bottom of the heel. As the condition progresses there may be a throbbing pain after getting off your feet or there may be soreness that radiates up the back of the leg. Pain may also radiate into the arch of the foot.
Causes
A sharp stabbing pain, like a nail going into the bottom of the heel when first stepping on the foot after getting out of bed or after sitting for period of time, is the most common description for plantar fasciitis or heel spur syndrome. Typically the pain eases off as the day goes on but it may not go away completely. A thick ligament that attaches to the bottom of the heel and runs the length of the foot to the toes can become inflamed and swollen at the attachment site. This tends to be an overuse type of injury where poor foot structure is involved; also, wearing of shoe gear that lacks adequate support (ie: worn out shoes, boots and flip-flops) and prolonged standing or walking are often implicated. A throbbing pain that gets worse as the day goes on and can be worse at night when laying in bed is most often associated with an irritated or entrapped nerve on the inside of the ankle or heel. This is similar to carpel tunnel syndrome in the wrist and hand. Approximately 7 / 10 patients with heel pain have a component of nerve entrapment as the cause of their heel pain. This is also one of the most common causes of chronic heel pain because it is often missed as a diagnosis. When nerve entrapment is considered to be a cause, painless neurosensory testing is performed with the Pressure Specified Sensory Device? (PSSD) at The Foot & Ankle Center, PC to determine the extent of compression. A less common cause of heel pain but a stress fracture is often considered in athletes, such as long distance runners, who have heel pain. Posterior Heel Pain (Retrocalcaneal) This is pain in the back of the heel that flares up when first starting an activity. It is often associated with a large bump that can be irritated by shoes. The Achilles tendon attaches to the back of the heel and, like on the bottom, this attachment site can often become inflamed; a spur may or may not be present. Another painful area is a sac of fluid (bursa) that sits between the tendon and bone to act as a cushion for the tendon. This bursa can become inflamed often leading to significant pain called retrocalcaneal bursitis.
Symptoms
The heel can be painful in many different ways, depending on the cause. Plantar fasciitis commonly causes intense heel pain along the bottom of the foot during the first few steps after getting out of bed in the morning. This heel pain often goes away once you start to walk around, but it may return in the late afternoon or evening. Although X-ray evidence suggests that about 10% of the general population has heels spurs, many of these people do not have any symptoms. In others, heel spurs cause pain and tenderness on the undersurface of the heel that worsen over several months. In a child, this condition causes pain and tenderness at the lower back portion of the heel. The affected heel is often sore to the touch but not obviously swollen. Bursitis involving the heel causes pain in the middle of the undersurface of the heel that worsens with prolonged standing and pain at the back of the heel that worsens if you bend your foot up or down. Pump bump, this condition causes a painful enlargement at the back of the heel, especially when wearing shoes that press against the back of the heel. Heel bruises, like bruises elsewhere in the body, may cause pain, mild swelling, soreness and a black-and-blue discoloration of the skin. Achilles tendonitis, this condition causes pain at the back of the heel where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel. The pain typically becomes worse if you exercise or play sports, and it often is followed by soreness, stiffness and mild swelling. A trapped nerve can cause pain, numbness or tingling almost anywhere at the back, inside or undersurface of the heel. In addition, there are often other symptoms, such as swelling or discoloration - if the trapped nerve was caused by a sprain, fracture or other injury.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will perform a physical exam and ask questions about your medical history and symptoms, such as have you had this type of heel pain before? When did your pain begin? Do you have pain upon your first steps in the morning or after your first steps after rest? Is the pain dull and aching or sharp and stabbing? Is it worse after exercise? Is it worse when standing? Did you fall or twist your ankle recently? Are you a runner? If so, how far and how often do you run? Do you walk or stand for long periods of time? What kind of shoes do you wear? Do you have any other symptoms? Your doctor may order a foot x-ray. You may need to see a physical therapist to learn exercises to stretch and strengthen your foot. Your doctor may recommend a night splint to help stretch your foot. Surgery may be recommended in some cases.
Non Surgical Treatment
There are many treatments for fasciitis. The most common initial treatment provided by the family doctor are anti-inflammatory medications. They may take the edge off the pain, but they don't often resolve the condition fully. Steroid injections, which deliver the medication directly to the most painful area, are usually more effective. Rest, ice, weight loss, taping, strapping, immobilization, physiotherapy, massage, stretching, heel cushions, acupuncture, night splints and extra-corporeal shock wave therapy all help some patients. Many patients, however, have a biomechanical cause such as excessively pronated feet to their complaint, and this may mean many of the treatments listed above will only provide temporary relief of fasciitis symptoms. When you stop the treatment, the pain often returns. This is why many cases of fasciitis respond well to orthoses, custom-made inserts that control the mechanical cause of the complaint. If you're considering orthoses, it's very important to have a podiatrist specializing in the field to examine you. There are many biomechanical factors to consider when assessing the need for literally dozens of types of devices available, so you need to have an expert to properly assess you. (Unfortunately, as is the case in many jurisdictions, there is no minimum standard of training required in British Columbia to make orthoses, and there are many fly-by-night operations around that employ salesmen with little, if any, training in understanding anatomy or foot function. The emphasis with these groups is on selling you some sort of device, rather than providing proper assessment, treatment and follow-up.
Surgical Treatment
It is rare to need an operation for heel pain. It would only be offered if all simpler treatments have failed and, in particular, you are a reasonable weight for your height and the stresses on your heel cannot be improved by modifying your activities or footwear. The aim of an operation is to release part of the plantar fascia from the heel bone and reduce the tension in it. Many surgeons would also explore and free the small nerves on the inner side of your heel as these are sometimes trapped by bands of tight tissue. This sort of surgery can be done through a cut about 3cm long on the inner side of your heel. Recently there has been a lot of interest in doing the operation by keyhole surgery, but this has not yet been proven to be effective and safe. Most people who have an operation are better afterwards, but it can take months to get the benefit of the operation and the wound can take a while to heal fully. Tingling or numbness on the side of the heel may occur after operation.
Prevention

Wear shoes that fit well, front, back and sides and have shock-absorbent soles, rigid uppers and supportive heel counters. Do not wear shoes with excessive wear on heels or soles. Prepare properly before exercising. Warm-up before running or walking, and do some stretching exercises afterward. Pace yourself when you participate in athletic activities. If overweight, try non weight-bearing activities such as swimming or cycling. Your podiatrist may also use taping or strapping to provide extra support for your foot. Orthoses (shoe inserts) specifically made to suit your needs may be also be prescribed.
Coping With Achilles Tendonitis Pain And discomfort
 The Achilles tendon attaches your calf muscles to your heel. You use this tendon to jump, walk, run, and stand on the balls of your feet. Continuous, intense physical activity, like running and jumping, can cause inflammation of the Achilles. This is known as Achilles tendonitis (also spelled tendinitis). Achilles tendonitis can often be treated at home using simple strategies. However, if home treatment doesn?t work, it is important to see a doctor. If your tendonitis gets worse, it can lead to a tendon tear. You may need medication to ease the pain or a surgical repair.
The Achilles tendon attaches your calf muscles to your heel. You use this tendon to jump, walk, run, and stand on the balls of your feet. Continuous, intense physical activity, like running and jumping, can cause inflammation of the Achilles. This is known as Achilles tendonitis (also spelled tendinitis). Achilles tendonitis can often be treated at home using simple strategies. However, if home treatment doesn?t work, it is important to see a doctor. If your tendonitis gets worse, it can lead to a tendon tear. You may need medication to ease the pain or a surgical repair.
Causes
Some of the causes of Achilles tendonitis include, overuse injury - this occurs when the Achilles tendon is stressed until it develops small tears. Runners seem to be the most susceptible. People who play sports that involve jumping, such as basketball, are also at increased risk. Arthritis - Achilles tendonitis can be a part of generalised inflammatory arthritis, such as ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis. In these conditions, both tendons can be affected. Foot problems - some people with flat feet or hyperpronated feet (feet that turn inward while walking) are prone to Achilles tendonitis. The flattened arch pulls on calf muscles and keeps the Achilles tendon under tight strain. This constant mechanical stress on the heel and tendon can cause inflammation, pain and swelling of the tendon. Being overweight can make the problem worse. Footwear - wearing shoes with minimal support while walking or running can increase the risk, as can wearing high heels. Overweight and obesity - being overweight places more strain on many parts of the body, including the Achilles tendon. Quinolone antibiotics - can in some instances be associated with inflammatory tenosynovitis and, if present, will often be bilateral (both Achilles), coming on soon after exposure to the drug.
Symptoms
There will be a gradual onset of achilles tendon pain over a period of weeks, or even months. The pain will come on during exercise and is constant throughout the training session. Pain will be felt in the achilles tendon when walking especially up hill or up stairs. This is because the achilles is having to stretch further than normal. There is likely to be stiffness in the Achilles tendon especially in the morning or after a long period of rest. This is thought to be due to adhesions between the tendon sheath and the tendon itself. Nodules or lumps may be found in the achilles tendon, particularly 2-4cm above the heel and the skin will appear red. Pain and tenderness will be felt when pressing in on the achilles tendon which is likely to appear thickened or swollen. A creaking sensation may be felt when press the fingers into the sides of the tendon and moving the ankle.This is known as crepitus.
Diagnosis
Laboratory studies usually are not necessary in evaluating and diagnosing an Achilles tendon rupture or injury, although evaluation may help to rule out some of the other possibilities in the differential diagnosis. Imaging studies. Plain radiography: Radiographs are more useful for ruling out other injuries than for ruling in Achilles tendon ruptures. Ultrasonography: Ultrasonography of the leg and thigh can help to evaluate the possibility of deep venous thrombosis and also can be used to rule out a Baker cyst; in experienced hands, ultrasonography can identify a ruptured Achilles tendon or the signs of tendinosis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI can facilitate definitive diagnosis of a disrupted tendon and can be used to distinguish between paratenonitis, tendinosis, and bursitis.
Nonsurgical Treatment
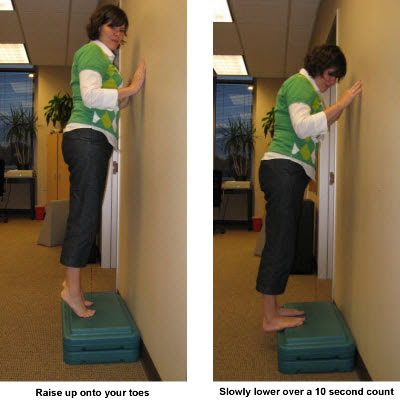
In most cases, nonsurgical treatment options will provide pain relief, although it may take a few months for symptoms to completely subside. Even with early treatment, the pain may last longer than 3 months. If you have had pain for several months before seeking treatment, it may take 6 months before treatment methods take effect. The first step in reducing pain is to decrease or even stop the activities that make the pain worse. If you regularly do high-impact exercises (such as running), switching to low-impact activities will put less stress on the Achilles tendon. Cross-training activities such as biking, elliptical exercise, and swimming are low-impact options to help you stay active. Placing ice on the most painful area of the Achilles tendon is helpful and can be done as needed throughout the day. This can be done for up to 20 minutes and should be stopped earlier if the skin becomes numb. A foam cup filled with water and then frozen creates a simple, reusable ice pack. After the water has frozen in the cup, tear off the rim of the cup. Then rub the ice on the Achilles tendon. With repeated use, a groove that fits the Achilles tendon will appear, creating a "custom-fit" ice pack. Drugs such as ibuprofen and naproxen reduce pain and swelling. They do not, however, reduce the thickening of the degenerated tendon. Using the medication for more than 1 month should be reviewed with your primary care doctor. The following exercise can help to strengthen the calf muscles and reduce stress on the Achilles tendon. Lean forward against a wall with one knee straight and the heel on the ground. Place the other leg in front, with the knee bent. To stretch the calf muscles and the heel cord, push your hips toward the wall in a controlled fashion. Hold the position for 10 seconds and relax. Repeat this exercise 20 times for each foot. A strong pull in the calf should be felt during the stretch. Physical therapy is very helpful in treating Achilles tendinitis. It has proven to work better for noninsertional tendinitis than for insertional tendinitis. Eccentric strengthening is defined as contracting (tightening) a muscle while it is getting longer. Eccentric strengthening exercises can cause damage to the Achilles tendon if they are not done correctly. At first, they should be performed under the supervision of a physical therapist. Once mastered with a therapist, the exercises can then be done at home. These exercises may cause some discomfort, however, it should not be unbearable. Stand at the edge of a stair, or a raised platform that is stable, with just the front half of your foot on the stair. This position will allow your heel to move up and down without hitting the stair. Care must be taken to ensure that you are balanced correctly to prevent falling and injury. Be sure to hold onto a railing to help you balance. Lift your heels off the ground then slowly lower your heels to the lowest point possible. Repeat this step 20 times. This exercise should be done in a slow, controlled fashion. Rapid movement can create the risk of damage to the tendon. As the pain improves, you can increase the difficulty level of the exercise by holding a small weight in each hand. This exercise is performed similarly to the bilateral heel drop, except that all your weight is focused on one leg. This should be done only after the bilateral heel drop has been mastered. Cortisone, a type of steroid, is a powerful anti-inflammatory medication. Cortisone injections into the Achilles tendon are rarely recommended because they can cause the tendon to rupture (tear).

Surgical Treatment
Surgery can be done to remove hardened fibrous tissue and repair any small tendon tears as a result of repetitive use injuries. This approach can also be used to help prevent an Achilles tendon rupture. If your Achilles tendon has already ruptured or torn, Achilles tendon surgery can be used to reattach the ends of the torn tendon. This approach is more thorough and definitive compared to non surgical treatment options discussed above. Surgical reattachment of the tendon also minimizes the change of re-rupturing the Achilles tendon.
Prevention
Warm up slowly by running at least one minute per mile slower than your usual pace for the first mile. Running backwards during your first mile is also a very effective way to warm up the Achilles, because doing so produces a gentle eccentric load that acts to strengthen the tendon. Runners should also avoid making sudden changes in mileage, and they should be particularly careful when wearing racing flats, as these shoes produce very rapid rates of pronation that increase the risk of Achilles tendon injury. If you have a tendency to be stiff, spend extra time stretching. If you?re overly flexible, perform eccentric load exercises preventively. Lastly, it is always important to control biomechanical alignment issues, either with proper running shoes and if necessary, stock or custom orthotics.
What Is Pain In The Heel
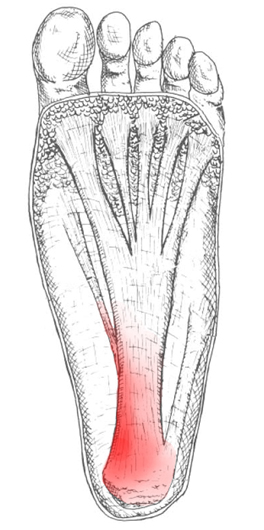
Overview
Foot pain affects nearly all people at one time or another. It can also lead to other musculoskeletal problems such as ankle, knee and back pain (Hill et al., 2008). This pain negatively affects one’s quality of life and ability to enjoy workouts and/or maintain a regular program of exercise. One of the most common sources of foot pain is plantar fasciitis, a condition where the connective tissue on the underside of the foot becomes irritated and painful as a result of an injury, overuse or misuse. The plantar fascia is a system of connective tissue that runs from your heel to just behind your toes. During weightbearing activities, such as walking or running, your body weight is transferred onto your foot from your heel to your toes (which results in your toes moving away from your heel). This spreading out of the foot places tension on the plantar fascia because it connects those two parts. If the tension on this structure is too great or is not dispersed evenly, the plantar fascia can develop microtears and become irritated and painful, resulting in a condition called plantar fasciitis.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis generally occurs over time, rather than being the result of a single event. Micro trauma from repetitive stress to the tissue often combines with a biomechanical deficiency of the foot to produce the condition. In addition, arthritic and metabolic factors may contribute to the development of this injury, (though they are unlikely to affect young athletes). A variety of training errors commonly lead to plantar fasciitis, particularly a rapid increase in either volume or intensity of athletic activity. Volume refers to the distance or time an athlete performs, while intensity refers to the pace of activity and/or the recovery time allowed following performance.
Symptoms
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis are pain on the bottom of the heel, pain in the arch of the foot, pain that is usually worse upon arising, pain that increases over a period of months. People with plantar fasciitis often describe the pain as worse when they get up in the morning or after they’ve been sitting for long periods of time. After a few minutes of walking the pain decreases, because walking stretches the fascia. For some people the pain subsides but returns after spending long periods of time on their feet.
Diagnosis
Most cases of plantar fasciitis are diagnosed by a health care provider who listens carefully to your description of symptoms. During an examination of your feet, your health care provider will have to press on the bottom of your feet, the area most likely to be painful in plantar fasciitis. Because the pain of plantar fasciitis has unique characteristics, pain upon rising, improvement after walking for several minutes, pain produced by pressure applied in a specific location on your foot but not with pressure in other areas, your health care provider will probably feel comfortable making the diagnosis based on your symptoms and a physical examination. Your health care provider may suggest that you have an X-ray of your foot to verify that there is no stress fracture causing your pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
About 90% of plantar fasciitis cases are self-limited and will improve within six months with conservative treatment and within a year regardless of treatment. Many treatments have been proposed for the treatment of plantar fasciitis. First-line conservative approaches include rest, heat, ice, calf-strengthening exercises, techniques to stretch the calf muscles, achilles tendon, and plantar fascia, weight reduction in the overweight or obese, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. NSAIDs are commonly used to treat plantar fasciitis, but fail to resolve the pain in 20% of people. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is an effective treatment modality for plantar fasciitis pain unresponsive to conservative nonsurgical measures for at least three months. Corticosteroid injections are sometimes used for cases of plantar fasciitis refractory to more conservative measures. The injections may be an effective modality for short-term pain relief up to one month, but studies failed to show effective pain relief after three months. Notable risks of corticosteroid injections for plantar fasciitis include plantar fascia rupture, skin infection, nerve or muscle injury, or atrophy of the plantar fat pad. Custom orthotic devices have been demonstrated as an effective method to reduce plantar fasciitis pain for up to 12 weeks. Night splints for 1-3 months are used to relieve plantar fasciitis pain that has persisted for six months. The night splints are designed to position and maintain the ankle in a neutral position thereby passively stretching the calf and plantar fascia overnight during sleep. Other treatment approaches may include supportive footwear, arch taping, and physical therapy.

Surgical Treatment
When more-conservative measures aren't working, your doctor might recommend steroid shots. Injecting a type of steroid medication into the tender area can provide temporary pain relief. Multiple injections aren't recommended because they can weaken your plantar fascia and possibly cause it to rupture, as well as shrink the fat pad covering your heel bone. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy. In this procedure, sound waves are directed at the area of heel pain to stimulate healing. It's usually used for chronic plantar fasciitis that hasn't responded to more-conservative treatments. This procedure may cause bruises, swelling, pain, numbness or tingling and has not been shown to be consistently effective. Surgery. Few people need surgery to detach the plantar fascia from the heel bone. It's generally an option only when the pain is severe and all else fails. Side effects include a weakening of the arch in your foot.
Stretching Exercises
The following exercises are commonly prescribed to patients with this condition. You should discuss the suitability of these exercises with your physiotherapist prior to beginning them. Generally, they should be performed 2 - 3 times daily and only provided they do not cause or increase symptoms. Your physiotherapist can advise when it is appropriate to begin the initial exercises and eventually progress to the intermediate and advanced exercises. As a general rule, addition of exercises or progression to more advanced exercises should take place provided there is no increase in symptoms. Calf Stretch with Towel. Begin this stretch in long sitting with your leg to be stretched in front of you. Your knee and back should be straight and a towel or rigid band placed around your foot as demonstrated. Using your foot, ankle and the towel, bring your toes towards your head until you feel a stretch in the back of your calf, Achilles tendon, plantar fascia or leg. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times at a mild to moderate stretch provided the exercise is pain free. Resistance Band Calf Strengthening. Begin this exercise with a resistance band around your foot as demonstrated and your foot and ankle held up towards your head. Slowly move your foot and ankle down against the resistance band as far as possible and comfortable without pain, tightening your calf muscle. Very slowly return back to the starting position. Repeat 10 - 20 times provided the exercise is pain free.
What Brings About Pain At The Heel To Flare Up

Overview
Plantar fasciitis is a very common condition resulting in pain under the heel which often radiates into the foot. We explain free of charge everything you need to know to cure your pain and prevent it from returning.
Causes
Each time we take a step forward, all of our body weight first rests on the heel of one foot. As our weight moves forward, the entire foot begins to bear the body's weight, and the foot flattens and this places a great deal of pressure and strain on the plantar fascia. There is very little elasticity to the plantar fascia, so as it stretches only slightly; it pulls on its attachment to the heel. If the foot is properly aligned this pull causes no problems. However, if the foot is "pronated" (the foot rolls outward at the ankle, causing a break down of the inner side of the shoe), the arch falls excessively, and this causes an abnormal stretching of the relatively inflexible plantar fascia, which in turn pulls abnormally hard on the heel. The same pathology occurs with "supination" (the rolling inward of the foot, causing a break down of the outer side of the shoe). Supinated feet are relatively in flexible; usually have a high arch, and a short or tight plantar fascia. Thus as weight is transferred from the heel to the remainder of the foot, the tight plantar fascia hardly stretches at all, and pulls with great force on its attachment to the heel.
Symptoms
The condition typically starts gradually with mild pain at the heel bone often referred to as a stone bruise. You're more likely to feel it after (not during) exercise. The pain classically occurs right after getting up in the morning and after a period of sitting. If you don't treat plantar fasciitis, it may become a chronic condition. You may not be able to keep up your level of activity, and you may develop symptoms of foot, knee, hip and back problems because plantar fasciitis can change the way you walk.
Diagnosis
Plantar fasciitis is usually diagnosed by your physiotherapist or sports doctor based on your symptoms, history and clinical examination. After confirming your plantar fasciitis they will investigate WHY you are likely to be predisposed to plantar fasciitis and develop a treatment plan to decrease your chance of future bouts. X-rays may show calcification within the plantar fascia or at its insertion into the calcaneus, which is known as a calcaneal or heel spur. Ultrasound scans and MRI are used to identify any plantar fasciitis tears, inflammation or calcification. Pathology tests (including screening for HLA B27 antigen) may identify spondyloarthritis, which can cause symptoms similar to plantar fasciitis.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of plantar fasciitis is sometimes a drawn out and frustrating process. A program of rehabilitation should be undertaken with the help of someone qualified and knowledgeable about the affliction. Typically, plantar fasciitis will require at least six weeks and up to six months of conservative care to be fully remedied. Should such efforts not provide relief to the athlete, more aggressive measures including surgery may be considered. The initial goals of physical therapy should be to increase the passive flexion of the foot and improve flexibility in the foot and ankle, eventually leading to a full return to normal function. Prolonged inactivity in vigorous sports is often the price to be paid for thorough recovery. Half measures can lead to a chronic condition, in some cases severely limiting athletic ability. As a large amount of time is spent in bed during sleeping hours, it is important to ensure that the sheets at the foot of the bed do not constrict the foot, leading to plantar flexion in which the foot is bent straight out with the toes pointing. This constricts and thereby shortens the gastroc complex, worsening the condition. A heating pad placed under the muscles of the calf for a few minutes prior to rising may help loosen tension, increase circulation in the lower leg and reduce pain. Also during sleep, a night splint may be used in order to hold the ankle joint in a neutral position. This will aid in the healing of the plantar fascia and ensure that the foot will not become flexed during the night.

Surgical Treatment
Like every surgical procedure, plantar fasciitis surgery carries some risks. Because of these risks your doctor will probably advise you to continue with the conventional treatments at least 6 months before giving you approval for surgery. Some health experts recommend home treatment as long as 12 months. If you can’t work because of your heel pain, can’t perform your everyday activities or your athletic career is in danger, you may consider a plantar fasciitis surgery earlier. But keep in mind that there is no guarantee that the pain will go away completely after surgery. Surgery is effective in many cases, however, 20 to 25 percent of patients continue to experience heel pain after having a plantar fasciitis surgery.
Prevention
Maintain a healthy weight. This minimizes the stress on your plantar fascia. Choose supportive shoes. Avoid high heels. Buy shoes with a low to moderate heel, good arch support and shock absorbency. Don't go barefoot, especially on hard surfaces. Don't wear worn-out athletic shoes. Replace your old athletic shoes before they stop supporting and cushioning your feet. If you're a runner, buy new shoes after about 500 miles of use. Change your sport. Try a low-impact sport, such as swimming or bicycling, instead of walking or jogging. Apply ice. Hold a cloth-covered ice pack over the area of pain for 15 to 20 minutes three or four times a day or after activity. Or try ice massage. Freeze a water-filled paper cup and roll it over the site of discomfort for about five to seven minutes. Regular ice massage can help reduce pain and inflammation. Stretch your arches. Simple home exercises can stretch your plantar fascia, Achilles tendon and calf muscles.